Pest Management Pathways
Topic outline
-
 There are no entrance requirements to the qualification or skill sets, nor are there prerequisite requirements for any of the pest management Units.
There are no entrance requirements to the qualification or skill sets, nor are there prerequisite requirements for any of the pest management Units. A person could complete one or more of the pest management skills sets and gain credit towards the complete qualification.
The pest management Industry supports the use of this qualification as a traineeship.
No Australian Apprenticeship pathways are declared for the qualificationLicensing and regulatory environments
The qualification and skill sets are equivalent and meet current regulatory requirements.
Pest management is subject to various and different licensing requirements across the States and Territories. The changes resulting from this project will not affect current licensing provisions. However, RTOs and other users of the qualification and skill sets will need to contact the relevant regulatory authority when seeking advice for candidates for licensing purposes. -
 Pest management technicians require well developed customer service skills as well as a sound knowledge of pests and integrated pest management.
Pest management technicians require well developed customer service skills as well as a sound knowledge of pests and integrated pest management. A pest management technician usually works alone, operating from a vehicle stocked with equipment and materials required for the particular types of jobs scheduled for each working day.
Whether working for a larger company – with a work order supplied by the business – or as an owner operator, the pest management technician must be self-managing in terms of ensuring the timeliness, efficiency, effectiveness, safety and quality of all aspects of the work at each site.The pest management qualification reflects the roles of pest management technicians who identify common urban pests, assess pest problems, consider pest management options, develop pest management plans, liaise with customers and implement pest management strategies.
In most cases, the technician will work alone and have responsibility for managing chemicals and equipment used in pest management as well as for a pest management vehicle, including the vehicle storage area. In the case of complex or high risk operations the technician may work as part of a team. -
Pest management is a licensed occupation, where the minimum requirement for operating as an independent pest manager is completion of the skill set CPPSS00023 Manage non-timber pests.
 There are two other skill sets used for licensing and these are:
There are two other skill sets used for licensing and these are:
CPPSS00022 Manage complex fumigation operations
CPPSS00025 Manage timber pests.
Many people employed in the pest management industry will complete one or more of these skill sets, depending on the core business of the company employing them, or if entering into the sector themselves, on which services they wish to offer as an owner operator.
The use of these skill sets for licensing sub-sectors of the industry goes some way to explaining the relatively low enrolment and completion figures for the Certificate III in Pest Management compared to the number of companies and technicians operating in the pest management sector.
Western Australia (WA) allows for a person who has achieved competence in the Unit CPPPMT3006 Manage pests by applying pesticides to obtain a provisional licence.
This provisional licence is valid for 12 months – to continue to practise as a pest management technician, provisional licence holders in WA must achieve competence in Certificate III in Urban Pest Management.
It is recommended that CPP Property Services Training Package users contact the relevant state or territory department(s) to confirm regulatory and licensing requirements that may apply.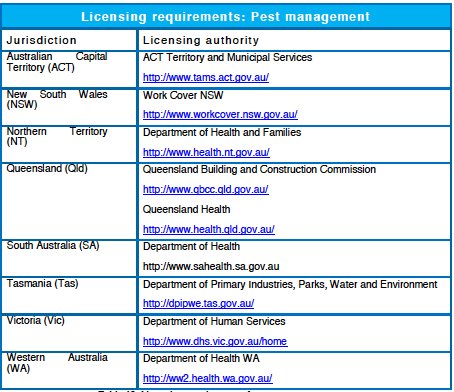
-
Health and safety issues in the pest management industry relate to:
- the use of pesticides and fumigants and their impacts on personal and public health
- pest behaviour and the impacts of pest actions
- hazards at work site environments.
Legislation and regulations, including work health and safety, public health and safety and environmental safety, govern the controlled use of pesticides and fumigants to manage pests and other organisms.
Pest management technicians need to be aware of the effects of pest behaviour and the impacts of their actions – such as dealing with spider bites or wasp stings – and the effects of termite action on wooden structures.
Pest management technicians must also assess each new work site that they visit for general hazards before inspecting for pests or treating the area.
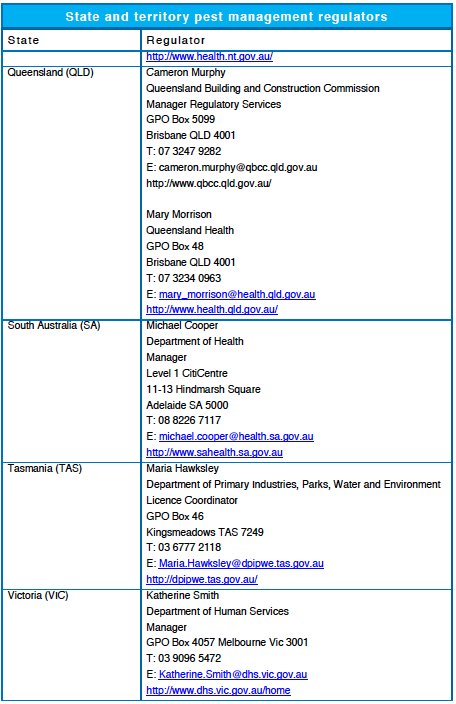
The licensing requirements in different states and territories reflect the need for pest management technicians to be competent in assessing risks and using pest management methods appropriately.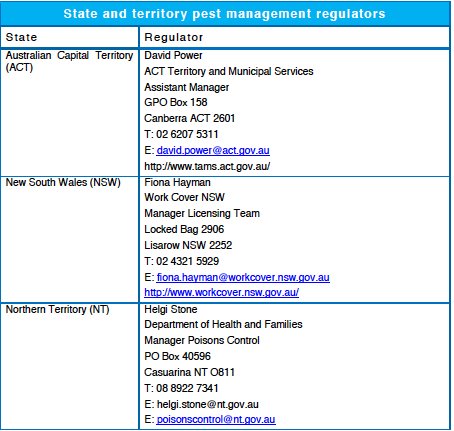
-